BrainVTA has developed a series of AAV products rAAV-1.2×HDV carrying 1.2 copies of the full-length HDV genome by taking advantage of the stable expression of AAV8 in host cells and strong hepatophilicity and combining a series of existing and self-developed (Patent No. CN111218446A) liver-specific promoters. This product can be used in combination with the AAV-HBV series to stably establish HBV/HDV co-infection and help the research of HDV replication mechanisms and the R&D of anti-HDV drugs.
Applications
● Establish of hepatitis D virus infection model
● Basic research on hepatitis D virus infection
● Development of antiviral drugs
Available AAV-1.2xHDV Particles
| Cat# | Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| PT-5700 | AAV-APOE/AAT1-HDV1.2x-bGfh poly A (AG) | Inquiry |
| PT-5699 | rAAV-APOE/AAT1-HDV2x-bGH polyA (G) | Inquiry |
| PT-4845 | rAAV-EAlb-hAAT1.2xHDV (G) | Inquiry |
| PT-4844 | rAAV-EAlb-hAAT1.2xHDV (AG) | Inquiry |
| PT-7394 | rAAV-APOE/AAT1-HDV1.2x(G)-bGH polyA | Inquiry |
| PT-7499 | rAAV-Ath1.2xHDV (G)-bGH polyA | Inquiry |
Our mature AAV-HDV platform can provide designing, cloning and high qualitative packaging service of the 1.2xHDV, 2xHDV, ect. products with quality assurance, fast delivery and competitive price.
Effect Verification
AAV-HBV and AAV-HDV were injected into 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice via tail vein in different combinations. HDV and HBV genomes in serum were quantified by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and qPCR, respectively, on days 7, 14, 21 and 45 after AAV injection. HDV genome could be detected in AAV-HBV/HDV co-infection group at 14 days and reached the highest level (A-C) at 21 days,meanwhile, Serum ALT levels were significantly increased (D), in addition, the gene expression of liver injury, necrosis, inflammation, proliferation, fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer increased significantly (E), and the liver tissue H&E staining also showed lobular inflammation (thick black arrow). Cytoplasmic swelling (thin black arrows) and "sandy" hepatic nuclei (thin white arrows) (F).
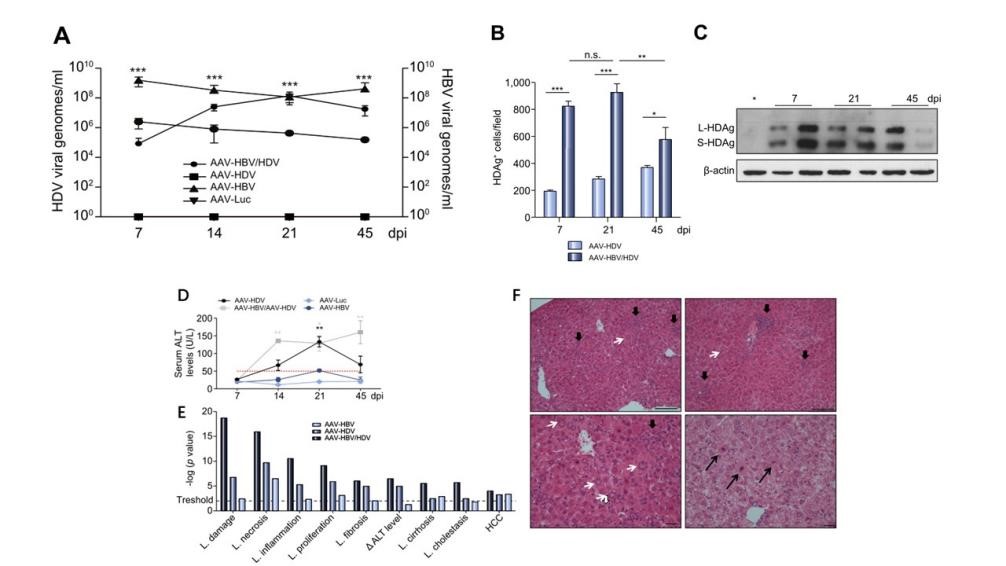 Fig1. Establishment of long-term HDV infection model in mice with AAV-HBV/HDV co-infection
Fig1. Establishment of long-term HDV infection model in mice with AAV-HBV/HDV co-infection
References
-
Global Hepatitis Report, 2017. WHO
-
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry. 2018 FDA
-
Christoph Seeger, and William S. Mason. Hepatitis B Virus Biology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews (2000). 51-68.
-
Haifeng Wang, Seahee Kim, and Wang-Shick Ryu. DDX3 DEAD-Box RNA Helicase Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcription by Incorporation into Nucleocapsids. Journal of General Virology (2009). 5815-5824.
-
Man-Young Cha, Dong-Kyun Ryu. Stimulation of hepatitis B virus genome replication by HBx is linked to both nuclear and cytoplasmic HBx expression. Journal of General Virology (2009). 90:978-986.
-
SUAREZ-AMARAN L, USAI C, DI SCALA M, et al. A new HDV mouse model identifies mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) as a key player in IFN-beta induction [J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(4): 669-79.
