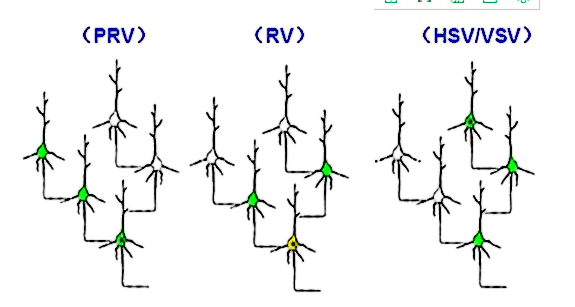
However, due to the ability to efficiently enter cells and deliver a variety of gene, genetically engineered recombinant viral vectors emerged as powerful tools for visualizing neural connectivity. The commonly used neurotropic virus, such as HSV ( Herpes simplex virus type 1), VSV (Vesicular stomatitis virus), PRV (pseudorabies virus) and RABV (rabies virus) can cross synapse from one cell to another, if we provide the protein that used for replicate. In addition, there are also SFV ( mark the fine morphology of in-situ neurons) and AAV viruses(as a helper virus to express exogenous genes or as a monosynaptic tracer with serotypes 1 ) that are used for neuronal tracing.
BrainVTA could offer VSV, PRV, RABV and HSV service to promote neuronal tracing studies.
Advantages
● Fast and high efficiency
● Strong background in neuronal tracing tool
● Hypotoxicity and strong signal
●The most competitive price
Table 1: Recombinant Viral Vectors Commonly Used in Neural Circuit Tracing
| Type | Virus name | Classification | Genomic type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-trans-synaptic | Adeno-associated virus, AAV | Parvoviridae | Single stranded DNA | |
| Canine adenovirus, CAV | Adenovirus | Double strands DNA | ||
| Semliki Forest virus, SFV | Togaviridae | Single stranded RNA | ||
| Rabies virus (Glycoprotein G-deleted), RV-ΔG | Rhabdoviridae | Single stranded RNA | ||
| Herpes simplex virus amplicon, HSV amplicon | Herpesviridae | Double strands DNA | ||
| Trans-synaptic | Anterograde, multisynaptic | Herpes simplex virus, HSV H129 | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA |
| Vesicular stomatitis virus, VSV | Rhabdoviridae | Single stranded RNA | ||
| Pseudorabies virus, PRV | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA | ||
| Retrograde, multisynaptic | Rabies virus, RV WT | Rhabdoviridae | Single stranded RNA | |
| Pseudorabies virus (TK-deleted), PRV-ΔTK | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA | ||
| Trans-monosynaptic | Rabies virus, RV-ΔG-EnvA | Rhabdoviridae | Single stranded RNA | |
| Herpes simplex virus (TK-deleted), HSV-ΔTK | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA | ||
| Adeno-associated virus serotype 1, AAV1 | Parvoviridae | Single stranded DNA | ||
| Rabies virus, RV-ΔG-EnvA | Rhabdoviridae | Single stranded RNA |
Please review Pseudorabies virus (PRV), Herpes simplex virus (HSV), Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV) for more detail information.
References
- Etessami R, Conzelmann KK, Fadai-Ghotbi B, Natelson B, Tsiang H, Ceccaldi PE. Spread and pathogenic characteristics of a G-deficient rabies virus recombinant: an in vitro and in vivo study. J Gen Virol. 2000 Sep;81(Pt 9):2147-53.
- Osakada F, Callaway EM. Design and generation of recombinant rabies virus vectors. Nat Protoc. 2013 Aug;8(8):1583-601.
- Callaway EM, Luo L. Monosynaptic Circuit Tracing with Glycoprotein-Deleted Rabies Viruses. J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;35(24):8979-85.

