COVID-19 Research Tools that BrainVTA provide
-
shRNA, overexpression, Gene editor for the proteins that the virus interacts with, like ACE2, S, S1, E, M.
-
Pre-made SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus particles encode luciferase, EGFP and mcherry in lentiviral and VSV.
-
Pre-made AAV and lentiviral particles that express S protein, TMPRSS2 and ACE2 receptor.
-
Effector cells: human ACE2 overexpression stable HEK293T and BHK cell lines.
SARS-CoV-2(2019nCoV) Pseudovirus (PSV) Based Research Field
1.Neutralization Assay
In the pseudovirus based neutralization assay, the inhibition of viral entry into cells by Neutralize Antibody is correlated to the decreased levels of luciferase or fluorescence (GFP and mcherry) signals in the ACE2 expression cells (HEK293T-hACE2 and BHK-hACE2).This method is simplicity, higher sensitivity and accuracy, suitability for high-throughput experiments. Also, no live virus is used during the test. Therefore, this method could be used as an alternative for safely conducting serologic studies in a rapid response.
-
To evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic monoclonal neutralizing antibodies.
-
To analyze and evaluate the neutralizing antibody levels of COVID-19 vaccines during the development phase and after future marketing.
- The dynamic change of neutralizing antibody level in COVID-19 convalescent patients.
-
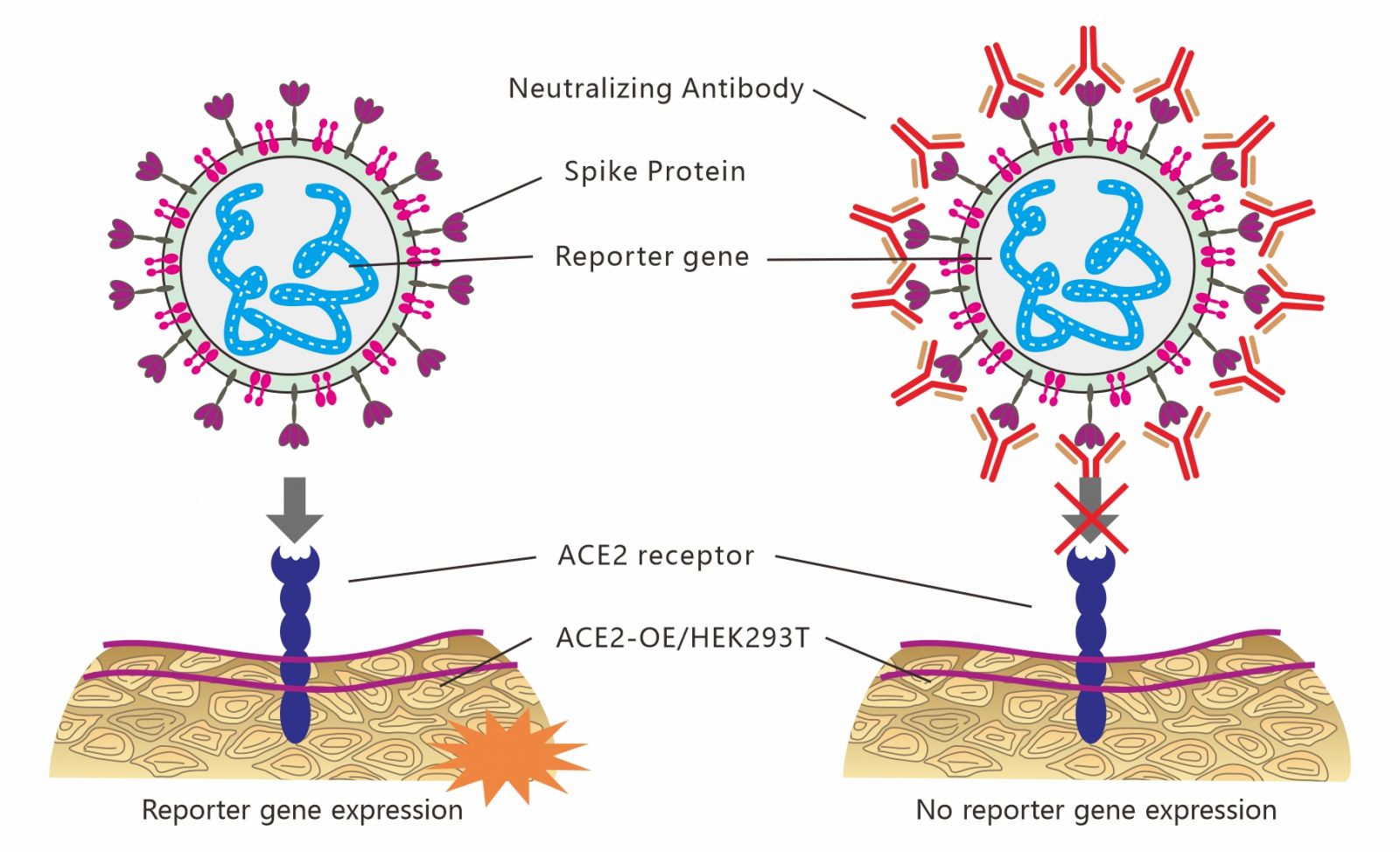
2.To construct a study model simulating SARS-COV-2 infected cells/animals.
.png)
COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Pseudovirus
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2-V03001 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-VSV-△G-EGFP | VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (WT)-EGFP | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-V03005 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-VSV-△G-Luciferase | VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (WT)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-LV-0046 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-LV-CMV-mcherry | HIV-1 Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (WT)-mcherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-LV-0052 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-LV-CMV-EGFP | HIV-1 Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (WT)-EGFP | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-LV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV-1 Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (WT)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-V03002 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-(D614G)-VSV-△G-mcherry | VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (D614G)-mcherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-K-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-(D614G)-rLV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV-1 Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (D614G)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-A-V03002 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(B1.1.7)-VSV-△G-mCherry | Alpha. VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (UK B.1.1.7; N501Y, A570D, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H)-mCherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-K-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(B.1.1.7)-rLV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV-1 Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (UK B.1.1.7; N501Y, A570D, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-B-V03002 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(SA-B.1.351)-VSV-△G-mCherry | Beta. VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (South African variant Δ3 B.1.351, 20H/501Y.V2, Beta; L18F, D80A, D215G, ΔL242/A243/L244, R246I, K417N, N501Y, E484K, D614G, A701V)-mCherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-B-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(SA-B.1.351)-LV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (South African variant Δ3 B.1.351, 20H/501Y.V2, Beta; L18F, D80A, D215G, ΔL242/A243/L244, R246I, K417N, N501Y, E484K, D614G, A701V)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| V04006 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(501Y.V2)-VSV-△G-mCherry | VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (South African variant B.1.351, 20C/501Y.V2; L18F, D80A, D215G, L242H, R246I, K417N, N501Y, E484K, D614G, A701V)-mCherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-K-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(501Y.V2)-rLV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (South African variant B.1.351, 20C/501Y.V2; L18F, D80A, D215G, L242H, R246I, K417N, N501Y, E484K, D614G, A701V)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| V04007 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(B1.1.617)-VSV-△G-mCherry | VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Indian variant B.1.617, RBD mutations only; L452R, E484Q, D614G)-mCherry | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-K-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(B1.1.617)-rLV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Indian variant B.1.617, RBD mutations only; L452R, E484Q, D614G)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-D-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(IN-B.1.617.2)-LV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Indian variant B.1.617.2; T19R, G142D, del156/157, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-K-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(IN-B.1.617.1)-LV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Indian variant B.1.617.1; G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, Q1071H)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-B-V03003 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(BZ-P.1)-VSV-CMV-Luciferase | Gamma. VSV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Brazilian variant: L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y, T1027I)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-G-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(BZ-P.1)-LV-CMV-Luciferase | Gamma. HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Brazilian variant: L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y, T1027I)-Luciferase | Inquiry |
| SARS-CoV-2-G-LV-0588 | PV-SARS-CoV-2-S(B.1.1.529)-LV-CMV-Luciferase | HIV Backbone, SARS-CoV-2 Spike (A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211-212, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F) | Inquiry |
Recombinant viral express SARS-COV-2-S, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 protein
| Vector | Cat. No. | Vector Name | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lentiviral vector | LV-0537 | rLV-CMV-SARS-CoV-2-S-2A-mCherry-WPRE | Inquiry |
| LV-0538 | rLV-Ef1a-ACE2-2A-EGFP-WPRE | Inquiry | |
| LV-0539 | rLV-Ef1a-ACE2-2A-EGFP--CMV-Puro-WPRE | Inquiry | |
| LV-0558 | rLV-CMV-TMPRSS2-2A-mCherry-WPRE | Inquiry | |
| LV-0559 | rLV-CMV-ACE2-2A-TMPRSS2-2A-EGFP-WPRE | Inquiry | |
| AAV vector | PT-2701 | rAAV-CMV-TMPRSS2-2A-BFP-WPRE | Inquiry |
| PT-2702 | rAAV-CMV-SARS-CoV-2-S-2A-mCherry-WPRE | Inquiry | |
| PT-2703 | rAAV-Ef1a-ACE2-2A-EGFP-WPRE | Inquiry |
Product Features
1.PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-VSV-△G-EGFP/mCherry
-
As the genome of the pseudovirus can replicate and the fluorescence signal will be enlarged, so pseudovirus in VSV has a high sensitivity.
-
Add PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-VSV-△G-EGFP/mCherry can only simulate the single infection process of COVID-19, and if you want to simulate the infection continuously, the S protein needs to be compensated by infecting LV/AAV that express it.
-
It can be handled in biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) and the fluorescence expression time is 7-8 hours.
2.PV-SARS-CoV-2-S-LV-CMV-EGFP/mCherry
-
Suitable for difficult to infect cells or tissues, such as stem cells, neurons, primary cells, etc.
-
Can only be used to simulate a single infection of COVID-19.
3.Recombinant lentivirus express SARS-COV-2-S, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 protein
-
Suitable for difficult to infect cells or tissues, such as stem cells, neurons, primary cells, etc.
-
Suitable for the establishment of cell model.
-
Suitable for the establishment of effector cells.
4.Recombinant AAV express SARS-COV-2-S, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 protein
-
Low immunogenicity and suitable for long-term expression.
-
Suitable for the establishment of animal models.
References
-
Jean K. Millet1, Tiffany Tang3, et al. Production of Pseudotyped Particles to Study Highly Pathogenic Coronaviruses in a Biosafety Level 2 Setting. J Vis Exp, doi:10.3791/59010 (2019).
-
Nie J, Li Q, Wu J, et al. Establishment and validation of a pseudovirus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2. Emerging Microbes & Infections. 2020;9(1):680-686.
-
Thomas T. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expression in the human heart: cause of a post-pandemic wave of heart failure. European Heart Journal. 2020;9(1):45.
-
Wrapp D, Wang NS, Corbett KS et al. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020;367:1260–1263.
